Sensor Types
For a detailed explanation of the following sensors, please read
Auto101 - Technical Articles - 15 Overview of Sensors & Actuators with questions
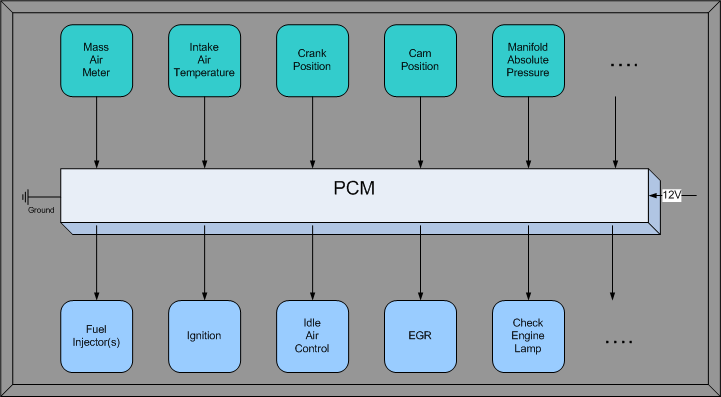
The following diagram depicts example inputs and outputs that a PCM uses to properly manage an automobile. Each manufacture has a preferred suite of inputs and outputs, preferred sensor types, and preferred actuator types. So, this section will discuss commonly used sensors.
Please use the following explanations described in this section to better understand how your particular car is configured.
Potentiometer
Resistive Sensor
- +/- Resistance
- Varies resistance based on position
- e.g. Throttle Position Sensor (TPS)
Thermistor
Resistive Sensor
- +/- Resistance
- Varies resistance based on Temperature
- e.g. Water Temperature Sensor
Piezo Resistive
Resistive Sensor
- +/- Resistance
- Varies resistance based on pressure
- e.g. Intake Manifold Pressure Sensor
Piezo Electric
Voltage Generating Sensor
- +/- Voltage
- Varies produced voltage based on vibration
- e.g. Knock Sensor
Zirconia-Dioxide
Voltage Generating Sensor
- +/- Voltage
- Produces voltage based on oxygen content
- e.g. Oxygen Sensor
Magnetic Inductance
Voltage Generating Sensor
- +/- Voltage
- Produces voltage as a magnet passed by a coil
- e.g. Wheel Speed Sensor
Physical Switch
Switch
- Open/Closes Circuit
- A ground or power is supplied based on switch position
- e.g. Door lock(momentary) or Headlight(toggle)
Phototransistor and LED
Switch
- Open/Close Circuit
- A ground is supplied based on light hitting a phototransistor
- e.g. Vehicle Speed Sensor
Reed Sensor
Switch
- Open/Close Circuit
- As a magnet passes by a reed, circuit is closed pulling-down circuit
- e.g. Vehicle Speed Sensor(speed) or Position Sensor(Inside TPS)